How Did Armenia So Badly Miscalculate Its War with Azerbaijan?
The National Interest
November 14, 2020
The long-term damage resulting from Armenia's miscalculations outlined are plain to see. While part of the damage is physical, even more significant is the mental damage: Armenia’s feeling of military superiority is now broken, and its feeling of isolation palpable.
Svante E. Cornell
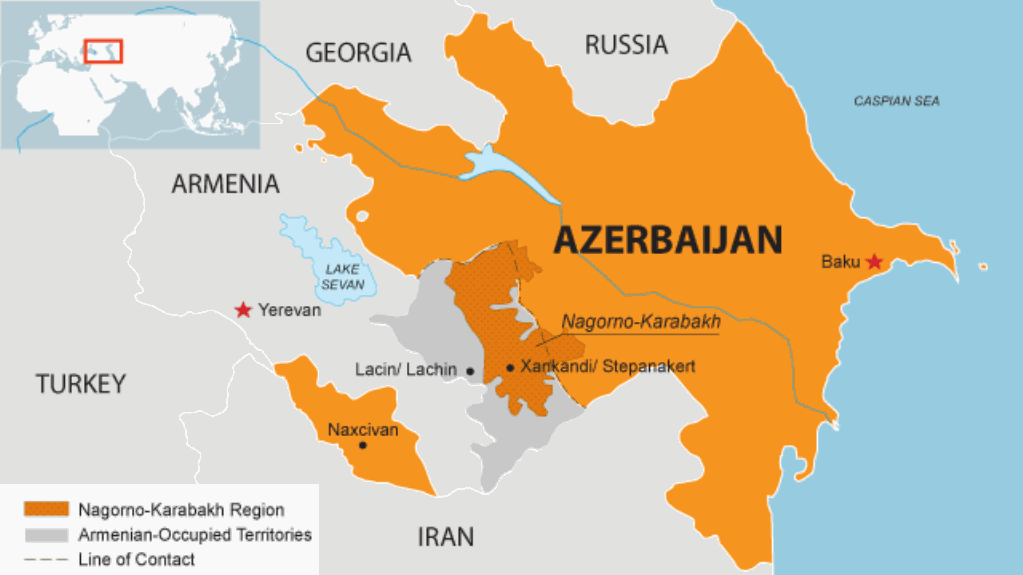
Since the Armenia-Azerbaijan war erupted again on Sept. 27, Armenia has suffered significant military setbacks at the hand of Azerbaijani forces. Not only has it lost most of the originally Azerbaijani-inhabited territories it occupied in 1993: Azerbaijani forces have made inroads into Nagorno-Karabakh, capturing the strategic and symbolic city of Shusha on Nov. 8.
Armenia seems to have been taken by surprise, something that is particularly puzzling given its increasingly assertive and belligerent rhetoric against Azerbaijan in the past several years. Why did the conflict not play out the way Armenian leaders imagined? The reason lies in a series of grave miscalculations, whereby Armenia’s leadership misread almost everything about this conflict: the broader international environment, the Russian response, Turkey’s role in the conflict, as well as the domestic dynamics of their adversary, Azerbaijan.
A deep paradox was always built into the Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict. Armenia has a third of Azerbaijan’s population, lacks its natural resources and key geopolitical location. But it won the war in the early 1990s, largely because of two factors: Azerbaijan’s internal turmoil and Russian backing for Yerevan. These factors helped Armenia win control over Nagorno-Karabakh as well as much larger territories surrounding that enclave, home to almost 750,000 Azerbaijanis who were forced to flee.
In Armenia, this victory laid the groundwork for a sense of military superiority that lasted until last month. But diplomatically, it soon became clear Armenia had bitten off more than it could chew. In large part because of the nation’s tragic history, Armenia had benefited from substantial international goodwill. But Yerevan’s territorial advances and ethnic cleansing of Azerbaijanis in 1993–94 changed that perception. By 1996, resolutions in international organizations like the UN and OSCE had made it clear that every other country in the world endorsed the return of all occupied territories to Azerbaijan and a solution to the conflict that would give the Armenians of Nagorno-Karabakh self-rule but deny them outright independence.
Meanwhile, the sheer scale of the territories Armenia occupied ensured that neither Azerbaijan’s leadership nor its society would come to terms with the situation. Instead, a powerful sense of revanchism built in Azerbaijan, and Baku invested a serious portion of the country’s windfall oil revenue into the country’s military. The growing disparity between the two countries became increasingly untenable: it was like a string that can only be pulled so far without breaking. Armenia responded by deepening its military dependence on Russia, which it saw as a guarantor of its military advances.
For some time, Armenia convinced itself that time was, in fact, on its side. After the twin shocks of 2008—the war in Georgia and the global financial crisis—its bet on Moscow even appeared rather shrewd. The West had proved unable to prevent the military defeat of its darling in the Caucasus, Georgia, and the financial crisis led to a gradual disengagement from the region on the part of western nations. Kosovo’s independence the same year created a second Albanian state in the Balkans, which Armenians saw as a precedent for Nagorno-Karabakh. Their hopes were further buoyed by Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea, which shared similarities with Armenia’s incorporation of Nagorno-Karabakh two decades earlier. As a result, Armenia came to view OSCE-led negotiations on the conflict mainly as a stalling tactic and did not appear to see the necessity of serious concessions in exchange for peace.
In April 2016, an escalation of tensions led to a “four-day” war in which Azerbaijan, for the first time since 1994, regained control of some occupied territories. Importantly, while Moscow negotiated a ceasefire after a few days, it did not intervene to stop or roll back Azerbaijan’s advances. This should have caused alarm bells to ring loudly in Yerevan. But, strangely, Armenia’s position instead hardened.
The first change was semantic. Many Armenians gradually began to refer to the occupied territories around Nagorno-Karabakh as “liberated territories”—a major shift, since they had previously been held as a security buffer and negotiating chip to secure Azerbaijani concessions on the status of Nagorno-Karabakh. No longer: Armenia now indicated it might not be willing to return these territories at all, ignoring the four UN Security Council resolutions that called for their “immediate and unconditional” return to Azerbaijan.
When Nikol Pashinyan acceded to power in spring 2018 following a “Velvet Revolution,” he first appeared willing to restart the peace process. Tellingly, the Azerbaijani elite welcomed his arrival: Baku passed up the opportunity to launch military operations during Armenia’s internal turmoil. Hoping to have a partner for peace, Baku appeared willing to give Pashinyan time to consolidate his power. When Aliyev and Pashinyan met in Dushanbe in October 2018, they agreed to de-escalate tensions. The prospects for peace looked better than they had in a long time.
But then something changed. In May 2019, Pashinyan repudiated the OSCE’s “Madrid Principles,” which had served as the basis for negotiations since 2007. He also sought to change the very format of negotiations, demanding the involvement of the local leadership in Nagorno-Karabakh in the talks. But speaking in August 2019 in the capital of Karabakh, he then stated that ”Karabakh is Armenia, period,” and rekindled the theme of unification of Armenia and Karabakh that had sparked the conflict in the late 1980s. These two statements were not only contradictory—if Karabakh is Armenia, why should it have a separate seat at the table—but also appeared to remove any space for negotiations on the territory’s status. There were other signs of the shift. Pashinyan’s wife, Anna Hakobyan, who had started the “women for peace” movement in 2018, this summer dressed up in military fatigues holding a submachine gun in an effort to promote military training for women. Their son also volunteered to serve in the occupied territories.
Armenia’s military strategy also changed: the same year, Defense Minister David Tonoyan—whose power and influence grew rapidly within the government—stated that Armenia now rejected the land-for-peace logic that had served as the basis for negotiations, and adopted instead a strategy pursuing “new wars for new territories.” This was coupled with assertive moves that changed the situation on the ground: Armenia relatively openly began to resettle ethnic Armenians from Syria and Lebanon into the occupied territories, creating new facts on the ground and adding to the sense of urgency in Baku. Yerevan’s position was best summarized in Pashinyan’s BBC Hard Talk interview of August 2020, which led exasperated host Stephen Sackur to conclude that “you clearly are not a peacemaker.”
But Armenian leaders then went even further: they took steps that, perhaps inadvertently, drew Turkey more directly into the dispute. When fighting erupted this July on the undisputed Armenia-Azerbaijan border way north of the conflict zone, it triggered fears in Turkey that Armenia was threatening the energy infrastructure in the very vicinity of the flareup carrying Azerbaijani oil and gas. Then, in early August, Armenia’s president and prime minister both made a point of commemorating the hundredth anniversary of the Treaty of Sèvres, which would have carved out an Armenian state out of eastern Turkey—a treaty that has for a century been a rallying cry for Turkish nationalists.
These developments suggest at least four grave miscalculations on the part of Armenian leaders.
First, the rhetoric of “liberated territories” reflects a deliberate attempt to take advantage of the weakening of international law and institutions. For two decades, Azerbaijan had centered its efforts on using diplomacy and international pressure to undo Armenia’s attempt to change international borders through military force. A weakening international order appeared to give Armenia a free hand to maintain its control over these lands indefinitely. What the Armenian leadership neglected to see is that this same international order also deterred Azerbaijan from abandoning diplomacy and pursuing a military solution. In 2019, President Ilham Aliyev noted that a world was emerging where “might is right,” intimating that Azerbaijan would act accordingly if it could not achieve its goals through diplomacy. Similarly, Armenia did not realize the implications of its failure to achieve international recognition for its occupation of Azerbaijani territory. As recent events have made clear, as long as the fighting remains centered on internationally recognized Azerbaijani territory, there is little that western or other powers will do aside from issuing habitual calls for restraint and negotiations.
Second, and perhaps more importantly, Armenia failed to internalize the fact that it could not take Russian support for granted. Russian influence over Armenia had grown so strong that Vladimir Putin saw little risk in also courting Ilham Aliyev and working to draw Azerbaijan into the Russian orbit. Students of Russian strategy had long understood that the Kremlin viewed its influence on Armenia as a lever to achieve influence over Georgia and Azerbaijan, both of which carry much greater geopolitical significance. Several years ago, Moscow began selling large amounts of weaponry to Azerbaijan. Baku certainly paid higher prices than Yerevan, but this move should have caused Armenian leaders to fundamentally question their strategy of dependence on Russia, as Russia also worked hard to entice Baku to join Russian-led organizations like the Eurasian Economic Union. But no such rethink happened in Yerevan, even after Russia failed to intervene during the 2016 flare up.
Like a poker player with a bad hand, Yerevan instead raised the stakes in a rather transparent bluff that Baku ultimately decided to call. While it remains possible that Moscow will step in and rescue Armenia, it is highly unlikely. Putin deeply distrusts Pashinyan and the way he came to power, and appears content to see him slapped in the face—perhaps in the hope that the ancien régime will return to power in Yerevan. It is notable that Ilham Aliyev this past August moved to purge the remaining pro-Russian forces inside his government and openly complained to Putin of Russian military supplies to Armenia. Putin’s cautious approach may reflect a need to play nice with Azerbaijan in order to retain some levers of influence over the most strategically important country in the Caucasus. Armenian leaders may have fundamentally failed to see that Russia, for all its bluster, is a declining power globally as well as regionally. While things could change, Russia so far appears to see little benefit from intervening decisively in this war, and even appears to seek to use the flareup to insert Russian peacekeepers into the conflict zone. All in all, Armenia was much more isolated than its rhetoric would have suggested.
Third, Armenian leaders failed to correctly analyze the growing linkages between the South Caucasus and the Middle East, and particularly Turkey’s role in the region. Since 2015, a powerful nationalist force has been ascendant within the Turkish state, and increasingly sets the parameters of Turkish foreign policy. President Recep Tayyip Erdogan—himself an Islamist rather than a nationalist—has been pushed in a more nationalist direction, which has led Ankara to challenge Moscow both in Syria and in Libya. For Armenia, the fact that Turkish drones outsmarted Russian air defenses, at least in the Libyan case, should have led to considerable alarm and signaled the need for great caution. In spite of clear warning signs, like Erdogan’s February 2020 statement that Karabakh matters as much to Turkey as it does to Azerbaijan, Armenian leaders failed entirely to anticipate the shift in Turkey’s position on the conflict. In fact, through steps like their embrace of the Treaty of Sèvres this summer, they accelerated that shift.
Finally, Armenian leaders failed to grasp the recent internal transformation of Azerbaijan. For many years, Ilham Aliyev was hamstrung by the presence of various oligarchs around him. But in the past several years, Azerbaijan’s leader has embarked on a far-reaching purge seeking to make the state more efficient. Aliyev was liberating himself from the shackles of the regime he took over from his father seventeen years ago. Armenian leaders appear not to have understood that Aliyev’s more assertive approach would affect Azerbaijan’s most pressing problem, the unresolved conflict over and the occupation of Azerbaijani territories, although Aliyev had many times signaled his great frustration over this situation.
Why, then, did Armenian leaders commit these grave miscalculations? Several reasons come to mind. The world has changed rapidly in recent years, requiring considerable flexibility and analytical skill to process the implications of the interaction between global and regional processes. Armenian leaders appear to have instead become complacent and internalized their own propaganda. Still, this does not account for the scale of their failure, which can only be explained by a deeper analysis of Armenian domestic politics.
It is now clear that Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan—who lacked political experience before being thrust into a position of power as leader of street protests in 2018—failed to comprehend the geopolitics of his country and region. But he was also constantly undermined by Armenia’s previous leadership, which in turn was aligned with the leadership in Karabakh, and maintained privileged relations with Moscow. This created a highly unstable situation, in which Pashinyan sought to outbid his rivals by adopting an increasingly hardline nationalist position to consolidate his power. Indeed, his call for unification was perhaps mainly targeted at the leadership in Karabakh and intended to shore up his popularity among Armenians there as well. If so, then he grossly underestimated the impact his words would have in Baku.
As of this writing, the parties have signed a cease-fire deal that cements Azerbaijan's military victory while maintaining some level of Armenian control over parts of Nagorno-Karabakh. The long-term damage resulting from Armenia's miscalculations outlined here is plain to see. While part of the damage is physical, even more significant is the mental damage: Armenia’s feeling of military superiority is now broken, and its feeling of isolation palpable. It should now be clear that Armenia can only be secure if it achieves lasting peace. Weakened as Pashinyan already was, it is difficult to see how he emerges unscathed from this episode, and calls for his resignation are mounting. More deeply, whether Pashinyan stays or goes, it remains to be seen whether Armenia will learn from this misadventure and embark upon a serious attempt to sue for peace.
Svante E. Cornell is the Director of the American Foreign Policy Council’s Central Asia-Caucasus Institute, co-founder of the Institute for Security and Development Policy and a Policy Advisor to JINSA’s Gemunder Center for Strategy.