Former Soviet States Are Distancing Themselves From Their Old Imperial Master
By Erica Marat and Johan Engvall
May 12, 2022
https://foreignpolicy.com/

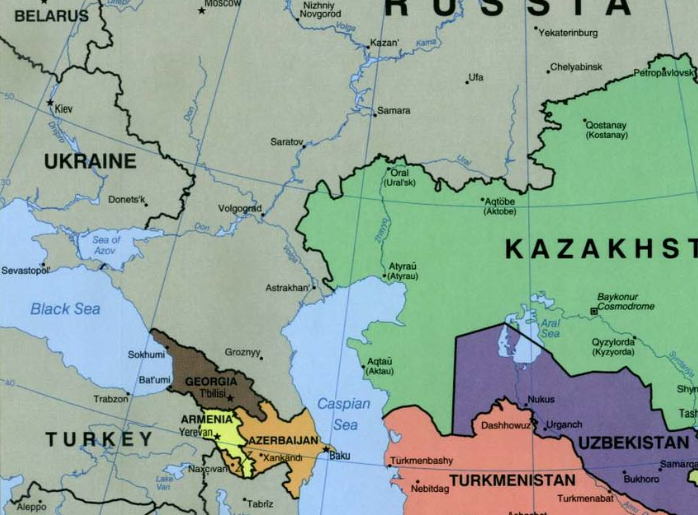
For many of Russia’s neighbors, the war in Ukraine has accelerated the process of breaking out of Moscow’s orbit and abandoning loyalty to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s regime. While governments from Moldova and Georgia to Kazakhstan are distancing themselves from Putin’s offensive in Ukraine, the war is also prompting a deeper reexamination of the meaning of the past in former Soviet territories. The idea of “brotherly nations” promoted by the Soviets is now overshadowed by the notion that Soviet Russia may have never pursued true equality with its neighbors—not now, nor a century ago when the Soviet empire was established through mass violence.
Thirty years after the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia is becoming just another neighbor in the eyes of Kazakhs, Georgians, Moldovans, and others.
Several governments have shown greater independence from Moscow than expected. Last month, Kazakhstan declared it wouldn’t hold a military parade to celebrate the Soviet interpretation of its World War II victory. Earlier, Kazakhstan reportedly also refused Russia’s request to supply troops in Ukraine. Both Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan expanded cooperation in rerouting energy supplies to Europe bypassing Russia. As explained by the Kazakh deputy foreign minister, “If there is a new Iron Curtain, we do not want to be behind it.”
The more a country is politically free and allows space for the critical reappraisal of its past, the less its public is likely to support Russia’s regional dominance.
Long-serving Uzbek Foreign Minister Abdulaziz Kamilov spoke out in support of Ukraine’s territorial integrity, including in Donetsk, Luhansk, and Crimea. Perhaps due to political pressure from Russia, he was later removed from his position and appointed to another post. Kyrgyzstan’s foreign minister was sacked as well—likely because of insufficient public support of Russia’s war.
In Moldova, which depends on Russian energy supplies and hosts hundreds of thousands of Ukrainian refugees, President Maia Sandu said her government is following Russia’s actions in Transnistria with “caution and vigilance.” A few days after the Russian invasion in Ukraine, Moldova applied for European Union membership, along with Georgia and Ukraine. Both Moldova and Georgia face Russian occupation of parts of their territories (Transnistria as well as South Ossetia and Abkhazia, respectively), which they don’t recognize as legitimate.
Acts of everyday resistance to Russia’s war in Ukraine in Central Asia and the South Caucasus vary from small businesses posting “Slava Ukraini” (Glory to Ukraine!) next to their products and civil society groups collecting humanitarian aid for Ukraine to members of the public wearing yellow and blue: the colors of the Ukrainian flag. The Russian war symbols Z and V are rare or banned by the state.
Seeing the Soviet regime as a colonialist government both unites nations around a joint history of trauma and builds resistance to Russian attempts to subjugate them. Russian modern imperial ambitions in Ukraine or Georgia look offensive in these countries. The more a country is politically free and allows space for the critical reappraisal of its past, the less its public is likely to support Russia’s regional dominance.
In Kazakhstan, a critical look at its history of mass starvation that killed millions of people have now spilled from academic discussions into the public. In Georgia and Kyrgyzstan, historians and activists now openly blame the Soviet regime for purging national elites. In Ukraine, a sharp turn against alignment with Russia in 2014 came as Moscow annexed Crimea and the occupied Donbas.
Reexamining the Soviet past is taking place despite the fact that most international scholarship still sees the Soviet empire as a modernizing power of a backward people, especially in Central Asia. The seeming equality among nations of the empire and its anti-capitalist stance earned a large following among the anticolonial left in both the West and especially in formerly colonized countries throughout Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
The war in Ukraine is revealing the human costs of the empire’s expansion today even in the face of grassroots resistance. Like Putin’s increasing control of Russia today, the Soviet system was totalitarian, controlling the everyday lives of its people and superimposing Russian culture on all ethnic groups.
Distancing themselves from a romanticized view of their Soviet pasts, these societies are now generating pressure for political change at home—challenging the type of post-Soviet authoritarian leadership model that has been common across the region and has its roots in totalitarian rule. In the past several years, protesters in Armenia, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, and Ukraine demanded reforms to post-Soviet state institutions, such as police and intelligence services that are designed to serve the political elite and not citizens.Anti-regime collective mobilization is a sign of a more politically engaged society that expects participation in decision-making and free elections. Ukraine’s resistance to Russian occupation is the ultimate example of how domestic pro-democracy mobilization rejects authoritarian rule.
In the face of this tide of new expectations, incumbent autocratic leaders are increasingly in peril. For example, in Russia’s closest ally, Belarus, President Aleksandr Lukashenko only managed to survive a prolonged popular uprising in the fall of 2020 once he received support from Putin. Lukashenko was able to suppress the protests, but the collective grievances of Belarus’s society have not been solved. In the early days of the invasion, Belarusian railway workers sabotaged Russia’s supply of equipment to Ukraine. The brave act damaged Russian logistics, preventing the Kremlin from moving troops and materiel forward.
Kazakhstan’s political setup is similar to Russia’s—a president sits at the top of a pyramid of power, doling out posts and assets to allies in return for loyalty and a cut of the spoils. But following Kazakhstan’s nationwide uprising in January, the country faces the test of transforming into a more representative political system. Despite decades of authoritarianism, citizens mobilized in historic protests to demand better economic opportunities and the end of the president’s unlimited political power. Many in Kazakhstan’s uprising were young people of the same age as the independent state itself. They now see themselves as agents of change, willing to risk more than their parents could stomach.
Moscow’s ability to influence national decision-making processes in former Soviet territories appears to be waning. Despite Moscow’s objections, Russian only remains a state language in Belarus, although it retains the status of an official language in Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. Azerbaijan switched from the Cyrillic to the Latin alphabet in the early 1990s while Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan are at different stages of the same transition.
Only four countries have joined the Russian-led Eurasian Economic Union, and the intergovernmental military alliance the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) has six members, Russia included. Both of these Russian-led organizations are likely to become ever more unpopular among political incumbents and the public. Even after the CSTO intervention in Kazakhstan in January, which helped President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev secure his hold on power, the Kazakh government has shown greater opposition to Moscow’s war than expected.
Russian political influence is also declining because Russian culture is losing its dominant position and has to compete with other worldviews for the hearts and minds of younger generations. These more diverse generations are formed by domestic as well as foreign influences, whether from Turkey, the Persian Gulf, or Europe. Traditional and nationalist-oriented values tend to resonate in more rural areas while liberal ideas and values are usually concentrated in urban centers. Large pro-Ukraine protests were held in Georgia, Kazakhstan, and Moldova. Even in countries like Kyrgyzstan, where the government banned antiwar protests, a few brave activists still filled the streets.
Rather than be pawns that are moved around on the Kremlin’s chessboard, Russia’s neighbors are increasingly turning into active players in the international arena.
Separation from Russia does not necessarily mean these countries will seek a closer alignment with the West. Political incumbents in Central Asia and the South Caucasus may be more inclined to seek closer ties with China and Turkey. Countries that depend on Russia’s political and military support—notably Armenia, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan—may still show careful support of close ties with Moscow. But even there, political leaders shied away from publicly siding with Putin’s rhetoric of “denazification” in Ukraine. The unpredictable consequences of Russia’s war might leave these states no other choice but to diversify their diplomatic relations.
Rather than be pawns that are moved around on the Kremlin’s chessboard, Russia’s neighbors are increasingly turning into active players in the international arena—and have not hesitated to play external powers against one another to extract maximum benefits. They prefer to maintain ties with many regional powers; Russia is becoming just another neighbor, along with the EU, China, Turkey, and Iran.
In that way, Central Asian countries are becoming more like other countries in Asia and Africa—searching for multilateralism rather than solely attaching themselves to one actor: Russia. The ability of these states to resist Moscow’s pressure to support the invasion of Ukraine would not have been possible without their long-standing efforts to preserve their sovereignty and identity themselves by diversifying their diplomatic alliances.
To understand the effectiveness of Russian power in the former Soviet space, it is no longer sufficient just to know the Kremlin’s intent. Former Soviet colonies are on the verge of breaking away from the last remaining legacies of Soviet rule. The war in Ukraine points at the need to consider countries formerly occupied by the Soviet regime as entities with their own complex domestic processes despite Russia’s efforts to direct and dominate them.
Many citizens of former Soviet states in Central Asia and the South Caucasus now see Russia as a belligerent neighbor engaging in genocidal violence rather than as an historic ally. Time is thus not on the side of Putin’s imperialistic and nationalist crusade to reassert Russia’s exclusive control over its neighboring countries—because Moscow’s neighborhood is no longer a collection of its former colonial subjects.
CACI Virtual Forum: Learning from Kazakhstan's January Crisis
In January 2022, Kazakhstan experienced an unprecedented political crisis. Though since overshadowed by events in Ukraine, it marked a turning point in the country’s history - one that will have considerable implications for the future of Central Asia. Those events are the subject of a new publication by Dr. Svante Cornell, and he will discuss his analysis and its major findings at our upcoming Forum.
Date: May 5, 2022, 9:00 AM EST.
Discussants:
- Svante Cornell, Director, Central Asia-Caucasus Institute at the American Foreign Policy Council
- Fred Starr, Chairman, Central Asia-Caucasus Institute at the American Foreign Policy Council

Learning from Kazakhstan's January Crisis

CACI Initiative on Religion and the Secular State in Central Asia and the Caucasus
In 2016, the Central Asia-Caucasus Institute & Silk Road Studies Program launched an initiative on documenting the interrelationship of religion and the secular state in the region. This initiative departed from the fact that little systematic reserch had been undertaken on the subject thus far. While there was and remains much commentary and criticism of religious policy in the region, there was no comprehensive analysis available on the interrelationship of religion and the state in any regional state, let alone the region as a whole. The result of this initiative has been the publication of six Silk Road Papers studying the matter in regional states, with more to come. In addition, work is ongoing on a volume putting the regional situation in the context of the Muslim world as a whole.
Case Studies
Each study below can be freely downloaded in PDF format.
Azerbaijan's Formula: Secular Governance and Civil Nationhood
By Svante E. Cornell, Halil Karaveli, and Boris Ajeganov
November 2016
 Religion and the Secular State in Kazakhstan
Religion and the Secular State in Kazakhstan
By Svante E. Cornell, S. Frederick Starr and Julian Tucker
April 2018
 Religion and the Secular State in Uzbekistan
Religion and the Secular State in Uzbekistan
Svante E. Cornell and Jacob Zenn
June 2018
 Religion and the Secular State in Kyrgyzstan
Religion and the Secular State in Kyrgyzstan
Johan Engvall
June 2020
 Religion and the Secular State in Turkmenistan
Religion and the Secular State in Turkmenistan
Victoria Clement
June 2020
Articles and Analyses
Svante E. Cornell, "Religion and the State in Central Asia," in Ilan Berman, ed., Wars of Ideas: Theology, Interpretation and Power in the Muslim World, Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, 2021.
Svante E. Cornell, "Central Asia: Where Did Islamic Radicalization Go?" in Religion, Conflict and Stability in the Former Soviet Union, eds. Katya Migacheva and Bryan Frederick, Arlington, VA: RAND Corporation, 2018.